Royal jelly proteins found to improve wound closure
07/16/2020 / By Evangelyn Rodriguez
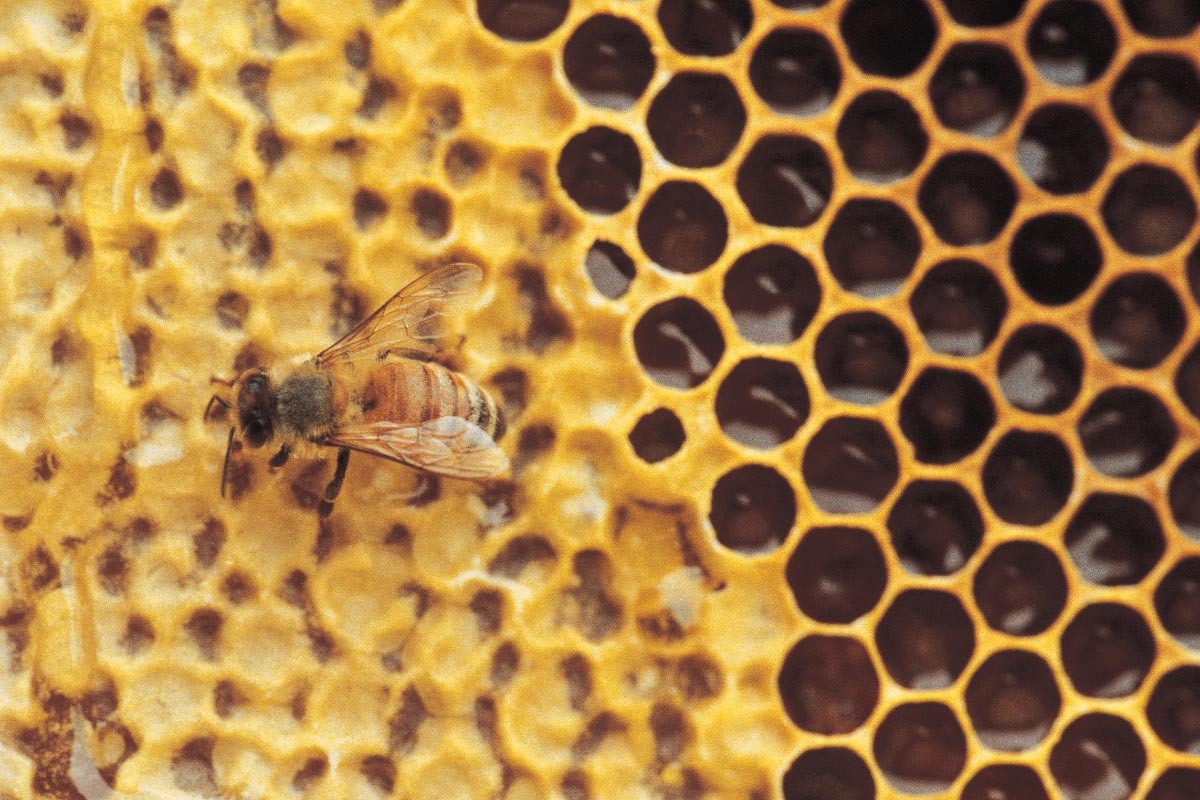

Royal jelly is a gelatinous substance synthesized by nurse honey bees. This secretion serves as food for young bees as well as for queen bees. Royal jelly consists of 60 to 70 percent water, about 11 to 23 percent carbohydrates, nine to 18 percent protein, four to eight percent lipids, and up to three percent miscellaneous compounds, such as salts, amino acids, vitamins or minerals.
According to studies on royal jelly, up to 90 percent of its total protein content is made up of major royal jelly proteins (MRJPs). So far, researchers have identified nine different MRJPs, and these macromolecules, along with chemicals like 10-hydroxy-2-decenoic acid (10-HDA, or the “queen bee acid”) and defensin-1, are credited with various health-promoting properties.
Some of the properties associated with royal jelly and its components include antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor, antioxidant, immunomodulatory and growth-promoting activities. It is also known to accelerate wound healing by suppressing inflammation, enhancing the production of growth factors and promoting the migration of specialized skin cells called fibroblasts and keratinocytes.
In a recent study, Chinese researchers explored the wound-repairing activity of royal jelly proteins using an in vitro scratch wound model. Their goal was to discover bioactive substances in royal jelly that create conditions conducive to natural wound healing, as well as to understand their mechanisms of action.
The researchers reported their findings in an article published in the journal BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine.
Major royal jelly proteins are behind this natural product’s wound-healing properties
In recent years, chronic wounds or skin injuries have become a considerable challenge due to the increasing morbidity of diseases like diabetes and other metabolic disorders.
Royal jelly, which has been reported to have numerous beneficial properties, is an age-old remedy for all kinds of wounds. However, its active components and their modes of action are still largely unknown.
For their experiment, the researchers fractionated water-soluble proteins extracted from royal jelly and examined their proliferative and migratory effects on human epidermal keratinocytes (HaCaT). The major cell components of the epidermis, keratinocytes are involved in the initiation, maintenance and completion of wound healing.
The researchers characterized and quantified the proteins in the bioactive fractions using label-free protein quantification method. Further analyses were done using bioinformatic tools.
The researchers reported that an active fraction that contained mainly MRJP2, MRJP3 and MRJP7 promoted the proliferation and migration of HaCaT cells without causing toxicity. This fraction also enhanced the growth of HaCaT cells during the first 48 hours of treatment.
Additionally, the researchers found that the fraction significantly increased the closure rates of the in vitro scratch wound model. Functional analysis of this fraction revealed that MRJP2, MRJP3 and MRJP7 are associated with carbohydrate transport and metabolism.
Based on these findings, the researchers concluded that royal jelly can improve wound closure by inducing cell proliferation and migration via MRJPs. As such, these proteins may prove useful for the development of novel and natural wound healing medications.
Other health benefits of royal jelly
Today, royal jelly is sold as a dietary supplement that helps treat a variety of illnesses, such as asthma, hay fever, insomnia, premenstrual syndrome, stomach ulcers, skin disorders and high cholesterol. It also often used as an ingredient for skincare products. Here are some of the benefits associated with royal jelly. (h/t to Healthline.com)
- It is a rich source of vitamins and trace minerals
- It has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties
- It can help lower cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of heart disease
- It aids in skin repair and wound healing
- It may help lower blood pressure
- It helps with blood sugar control
- It supports healthy brain function
- It may help treat chronic dry eyes
- It helps keep the skin healthy and younger-looking
- It helps boost the immune system
- It may help relieve some side effects of chemotherapy
- It can help reduce the symptoms of menopause
Royal jelly is a natural product that’s generally considered to be safe for consumption. It also has a long history of use as a natural remedy so you can have no doubts about its effectiveness. However, certain royal jelly products may not be as pure and clean as they ought to be. Products contaminated with pesticides have been reported to trigger allergic reactions. To avoid adverse reactions, purchase high-quality royal jelly only from trusted sources.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: alternative medicine, biotin supplements, cosmetics, honey bees, keratinocytes, natural cures, natural medicine, remedies, research, Royal jelly, royal jelly proteins, skin care, supplements, wound closure, Wound Healing
RECENT NEWS & ARTICLES
EmergencyMedicine.News is a fact-based public education website published by Emergency Medicine News Features, LLC.
All content copyright © 2018 by Emergency Medicine News Features, LLC.
Contact Us with Tips or Corrections
All trademarks, registered trademarks and servicemarks mentioned on this site are the property of their respective owners.